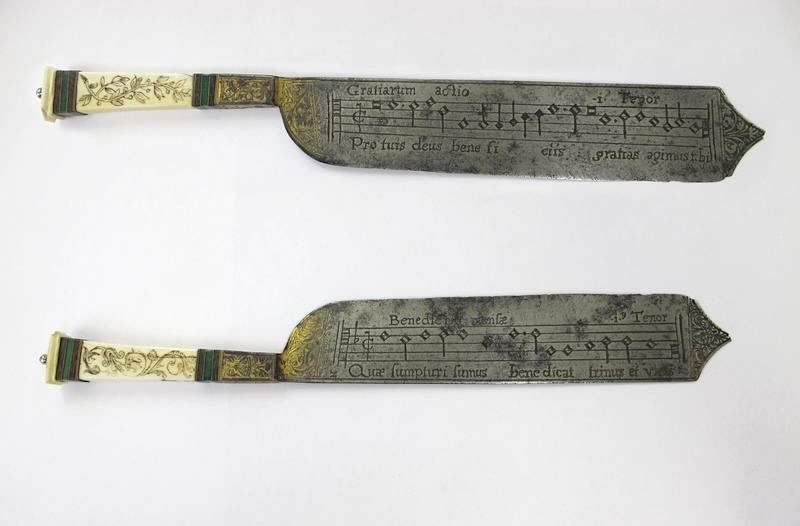

Image courtesy of The Victoria and Albert Museum
On any given weekend, in any part of the state where I live, you can find yourself standing in a hall full of knives, if that’s the kind of thing you like to do. It is a very niche kind of experience. Not so in some other weapons expos—like the Arms and Armor galleries at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, where everyone, from the most warlike to the staunchest of pacifists, stands in awe at the intricate ornamentation and incredibly deft craftsmanship on display in the suits of armor, lances, shields, and lots and lots of knives.
We must acknowledge in such a space that the worlds of art and of killing for fame and profit were never very far apart during Europe’s late Medieval and Renaissance periods. Yet we encounter many similar artisanal instruments from the time, just as finely tuned, but made for far less belligerent purposes.
As Maya Corry of the Fitzwilliam Museum in Cambridge—an institution with its own impressive arms and armor collection—comments in the video above (at 2:30), one unusual kind of 16th century knife meant for the table, not the battlefield, offers “insight into that harmonious, audible aspect of family devotions,” prayer and song.
From the collection of the Fitzwilliam Museum, in Cambridge. (Johan Oosterman )
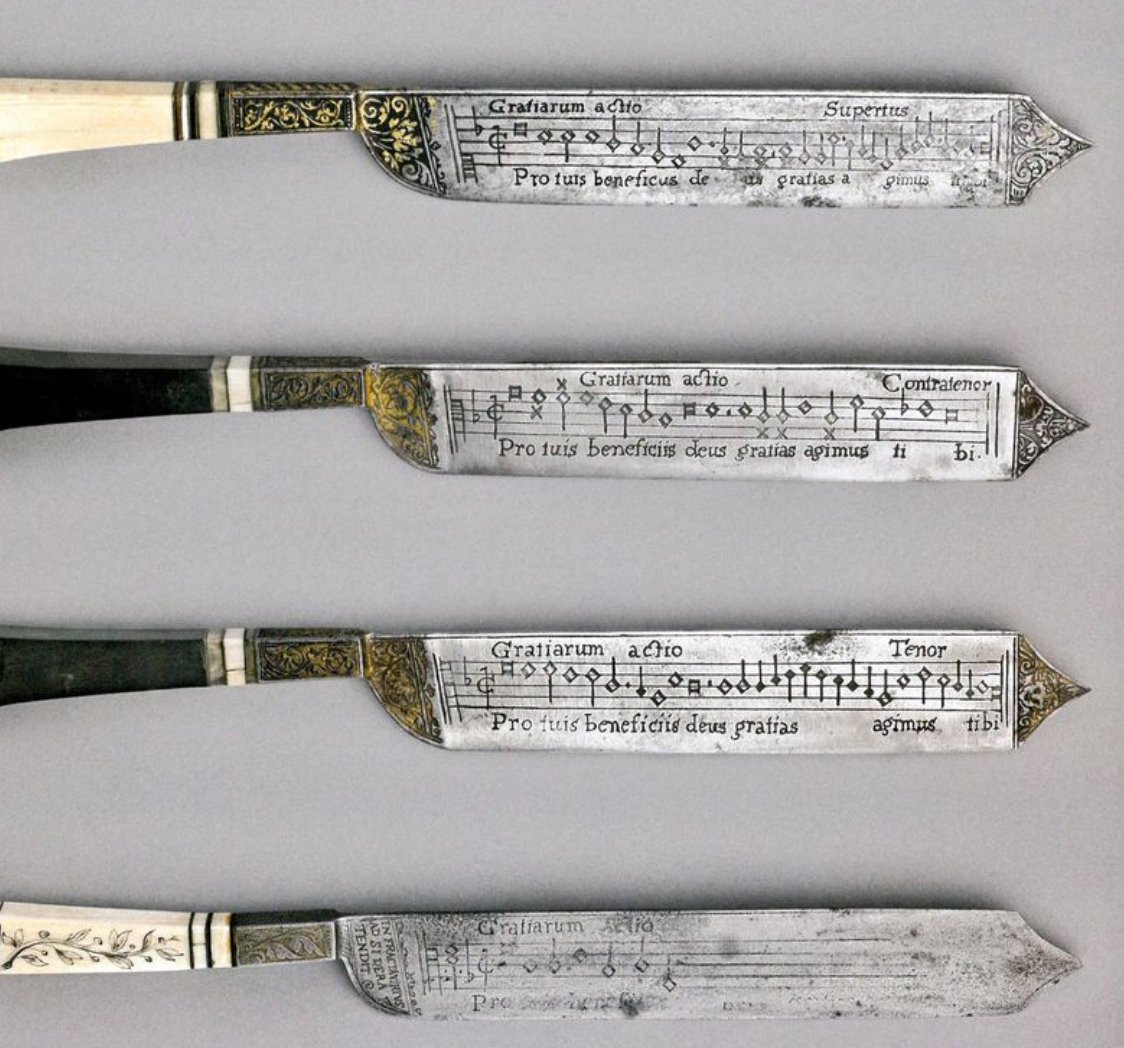
These knives, which have musical scores engraved in their blades, brought a table together in singing their prayers, and may have been used to carve the lamb or beef in their “striking balance of decorative and utilitarian function.” At least historians think such “notation knives,” which date from the early 1500s, were used at banquets. “The sharp, wide steel would have been ideal for cutting and serving meat,” writes Eliza Grace Martin at the WQXR blog, “and the accentuated tip would have made for a perfect skewer.” But as Kristen Kalber, curator at the Victoria and Albert Museum, which houses the knives at the top of the post, tells us “diners in very grand feasts didn’t cut their own meat.” It’s unlikely they would have sung from the bloody knives held by their servants.
The knives’ true purpose “remains a mystery,” Martin remarks, like many “rituals of the Renaissance table.” Victoria and Albert Museum curator Kirstin Kennedy admits in the video above that “we are not entirely sure” what the “splendid knife” she holds was used for. But we do know that each knife had a different piece of music on each side, and that a set of them together contained different harmony parts in order to turn a roomful of diners into a chorus. One set of blades had the grace on one side, with the inscription, “the blessing of the table. May the three-in-one bless that which we are about to eat.” The other side holds the benediction, to be sung after the dinner: “The saying of grace. We give thanks to you God for your generosity.”
Common enough verbiage for any household in Renaissance Europe, but when sung, at least by a chorus from the Royal College of Music, who recreated the music and made the recordings here, the prayers are superbly graceful. Above, hear one version of the Grace and Benediction from the Victoria and Albert Museum knives; below, hear a second version. You can hear a captivating set of choral prayers from the Fitzwilliam Museum knives at WQXR’s site, recorded for the Fitzwilliam’s “Madonnas & Miracles” exhibit. We are as unlikely now to encounter singing kitchen knives as we are to run into a horse and rider bearing 100 pounds of finely-wrought wearable steel sculpture. Such strange artifacts seem to speak of a strange people who valued beauty whether carving up the main course or cutting down their enemies.
Note: An earlier version of this post appeared on our site in 2017.
If you would like to sign up for Open Culture’s free email newsletter, please find it here.
If you would like to support the mission of Open Culture, consider making a donation to our site. It’s hard to rely 100% on ads, and your contributions will help us continue providing the best free cultural and educational materials to learners everywhere. You can contribute through PayPal, Patreon, and Venmo (@openculture). Thanks!
Josh Jones is a writer and musician based in Durham, NC. Follow him at @jdmagness

0 Commentaires